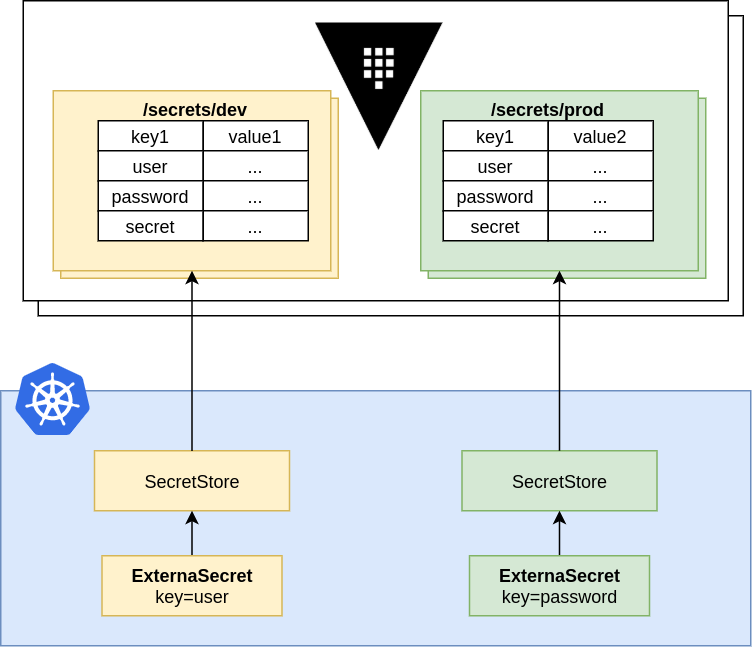
The basic ExternalSecret example is referencing a ClusterSecretStore while all of the examples of configuring a provider are a /SecretStore/. This means that a new user try to cut'n'paste the examples will be unable to create a working demo without reading the API reference.
3.8 KiB
Hashicorp Vault
External Secrets Operator integrates with HashiCorp Vault for secret management. Vault itself implements lots of different secret engines, as of now we only support the KV Secrets Engine.
Example
First, create a SecretStore with a vault backend. For the sake of simplicity we'll use a static token root:
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1alpha1
kind: SecretStore
metadata:
name: vault-backend
spec:
provider:
vault:
server: "http://my.vault.server:8200"
path: "secret"
version: "v2"
auth:
# points to a secret that contains a vault token
# https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/auth/token
tokenSecretRef:
name: "vault-token"
namespace: "default"
key: "token"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: vault-token
data:
token: cm9vdA== # "root"
Then create a simple k/v pair at path secret/foo:
vault kv put secret/foo my-value=s3cr3t
Now create a ExternalSecret that uses the above SecretStore:
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1alpha1
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: vault-example
spec:
refreshInterval: "15s"
secretStoreRef:
name: vault-backend
kind: SecretStore
target:
name: example-sync
data:
- secretKey: foobar
remoteRef:
key: secret/foo
property: my-value
---
# will create a secret with:
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-sync
data:
foobar: czNjcjN0
Limitations
Vault supports only simple key/value pairs - nested objects are not supported. Hence specifying gjson properties like other providers support it is not supported.
Authentication
We support five different modes for authentication: token-based, appRole, kubernetes-native, ldap and jwt/odic, each one comes with it's own trade-offs. Depending on the authentication method you need to adapt your environment.
Token-based authentication
A static token is stored in a Kind=Secret and is used to authenticate with vault.
{% include 'vault-token-store.yaml' %}
AppRole authentication example
AppRole authentication reads the secret id from a
Kind=Secret and uses the specified roleId to aquire a temporary token to fetch secrets.
{% include 'vault-approle-store.yaml' %}
Kubernetes authentication
Kubernetes-native authentication has three options of optaining credentials for vault:
- by using a service account jwt referenced in
serviceAccountRef - by using the jwt from a
Kind=Secretreferenced by thesecretRef - by using transient credentials from the mounted service account token within the external-secrets operator
{% include 'vault-kubernetes-store.yaml' %}
LDAP authentication
LDAP authentication uses
username/password pair to get an access token. Username is stored directly in
a Kind=SecretStore or Kind=ClusterSecretStore resource, password is stored
in a Kind=Secret referenced by the secretRef.
{% include 'vault-ldap-store.yaml' %}
JWT/OIDC authentication
JWT/OIDC uses a
JWT token stored in a Kind=Secret and referenced by the
secretRef. Optionally a role field can be defined in a Kind=SecretStore
or Kind=ClusterSecretStore resource.
{% include 'vault-jwt-store.yaml' %}