This removes the need for an intermediary Kind=ExternalSecret and Kind=Secret when using a generator. Signed-off-by: Moritz Johner <beller.moritz@googlemail.com>
3.1 KiB
Contrary to what ExternalSecret does by pulling secrets from secret providers and creating kind=Secret in your cluster, PushSecret reads a local kind=Secret and pushes its content to a secret provider.
The update behavior of PushSecret is controlled by spec.updatePolicy. The default policy is Replace, such that secrets are overwritten in the provider, regardless of whether there already is a secret present in the provider at the given location. If you do not want PushSecret to overwrite existing secrets in the provider, you can set spec.UpdatePolicy to IfNotExists. With this policy, the provider becomes the source of truth. Please note that with using spec.updatePolicy=IfNotExists it is possible that the secret value referenced by the PushSecret within the cluster differs from the secret value at the given location in the provider.
By default, the secret created in the secret provided will not be deleted even after deleting the PushSecret, unless you set spec.deletionPolicy to Delete.
{% include 'full-pushsecret.yaml' %}
Backup use case
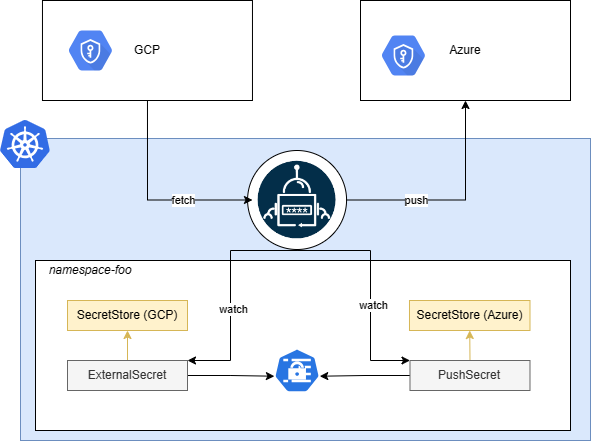
An interesting use case for kind=PushSecret is backing up your current secret from one provider to another one.
Imagine you have your secrets in GCP and you want to back them up in Azure Key Vault. You would then create a SecretStore for each provider, and an ExternalSecret to pull the secrets from GCP. This will generate a kind=Secret in your cluster that you can use as the source of a PushSecret configured with the Azure SecretStore.
Pushing the whole secret
There are two ways to push an entire secret without defining all keys individually.
By leaving off the secret key and remote property options.
{% include 'full-pushsecret-no-key-no-property.yaml' %}
This will result in all keys being pushed as they are into the remote location.
By leaving off the secret key but setting the remote property option.
{% include 'full-pushsecret-no-key-with-property.yaml' %}
This will marshal the entire secret data and push it into this single property as a JSON object.
!!! warning inline This should ONLY be done if the secret data is marshal-able. Values like, binary data cannot be marshaled and will result in error or invalid secret data.
Key conversion strategy
You can also set data[*].conversionStrategy: ReverseUnicode to reverse the invalid character replaced by the conversionStrategy: Unicode configuration in the ExternalSecret object as documented here.
Rotate Secrets
You can use ESO to rotate secrets by using the PushSecret and Generator resources. ESO will consult the Kind=Generator to generate a new secret and then ESO will store it.
Every spec.refreshInterval the secret will be rotated and the value will be replaced in the store unless spec.updatePolicy=IfNotExist is set. Then ESO will generate the secret once and won't rotate it.
{% include 'pushsecret-generator-rotation-example.yaml' %}