Signed-off-by: Dominik Zeiger <dominik@zeiger.biz> Signed-off-by: Dominik Zeiger <dominik@zeiger.biz>
2.3 KiB
Gitlab Variables
External Secrets Operator integrates with Gitlab to sync Gitlab Project Variables API and/or Gitlab Group Variables API to secrets held on the Kubernetes cluster.
Configuring Gitlab
The Gitlab API requires an access token, project ID and/or groupIDs.
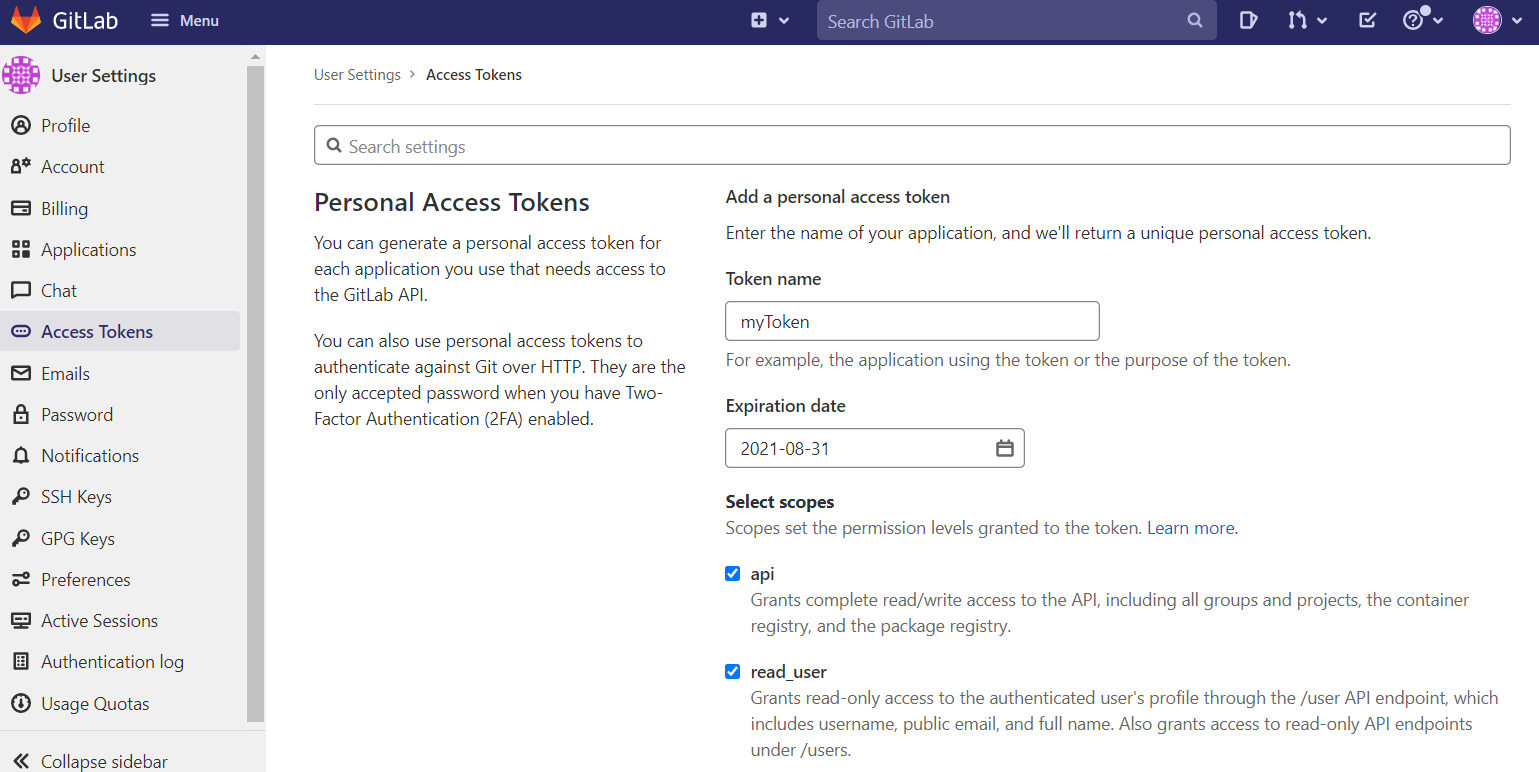
To create a new access token, go to your user settings and select 'access tokens'. Give your token a name, expiration date, and select the permissions required (Note 'api' is required).
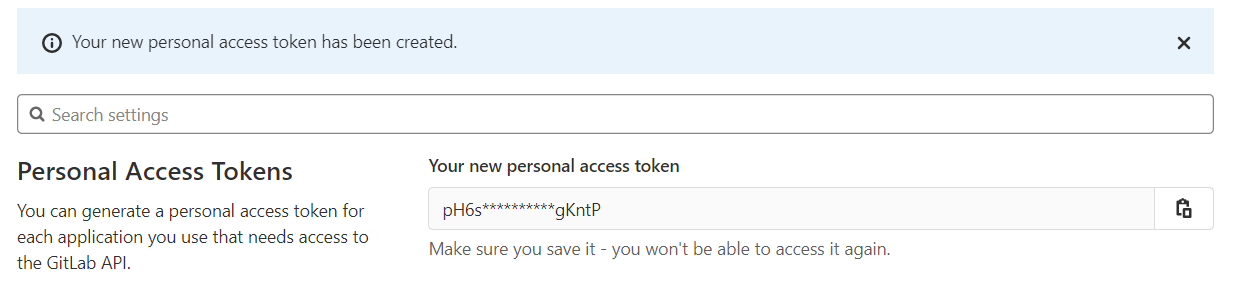
Click 'Create personal access token', and your token will be generated and displayed on screen. Copy or save this token since you can't access it again.
Access Token secret
Create a secret containing your access token:
{% include 'gitlab-credentials-secret.yaml' %}
Configuring the secret store
Be sure the gitlab provider is listed in the Kind=SecretStore and the ProjectID is set. If you are not using https://gitlab.com, you must set the url field as well.
In order to sync group variables inheritFromGroups must be true or groupIDs have to be defined.
In case you have defined multiple environments in Gitlab, the secret store should be constrained to a specific environment_scope.
{% include 'gitlab-secret-store.yaml' %}
NOTE: In case of a ClusterSecretStore, Be sure to provide namespace in accessToken with the namespace where the secret resides.
Your project ID can be found on your project's page.

Creating external secret
To sync a Gitlab variable to a secret on the Kubernetes cluster, a Kind=ExternalSecret is needed.
{% include 'gitlab-external-secret.yaml' %}
Using DataFrom
DataFrom can be used to get a variable as a JSON string and attempt to parse it.
{% include 'gitlab-external-secret-json.yaml' %}
Getting the Kubernetes secret
The operator will fetch the project variable and inject it as a Kind=Secret.
kubectl get secret gitlab-secret-to-create -o jsonpath='{.data.secretKey}' | base64 -d