*[documentation](/README.md#documentation) / Writing Policies*
# Writing Policies
The following picture shows the structure of a Kyverno Policy:
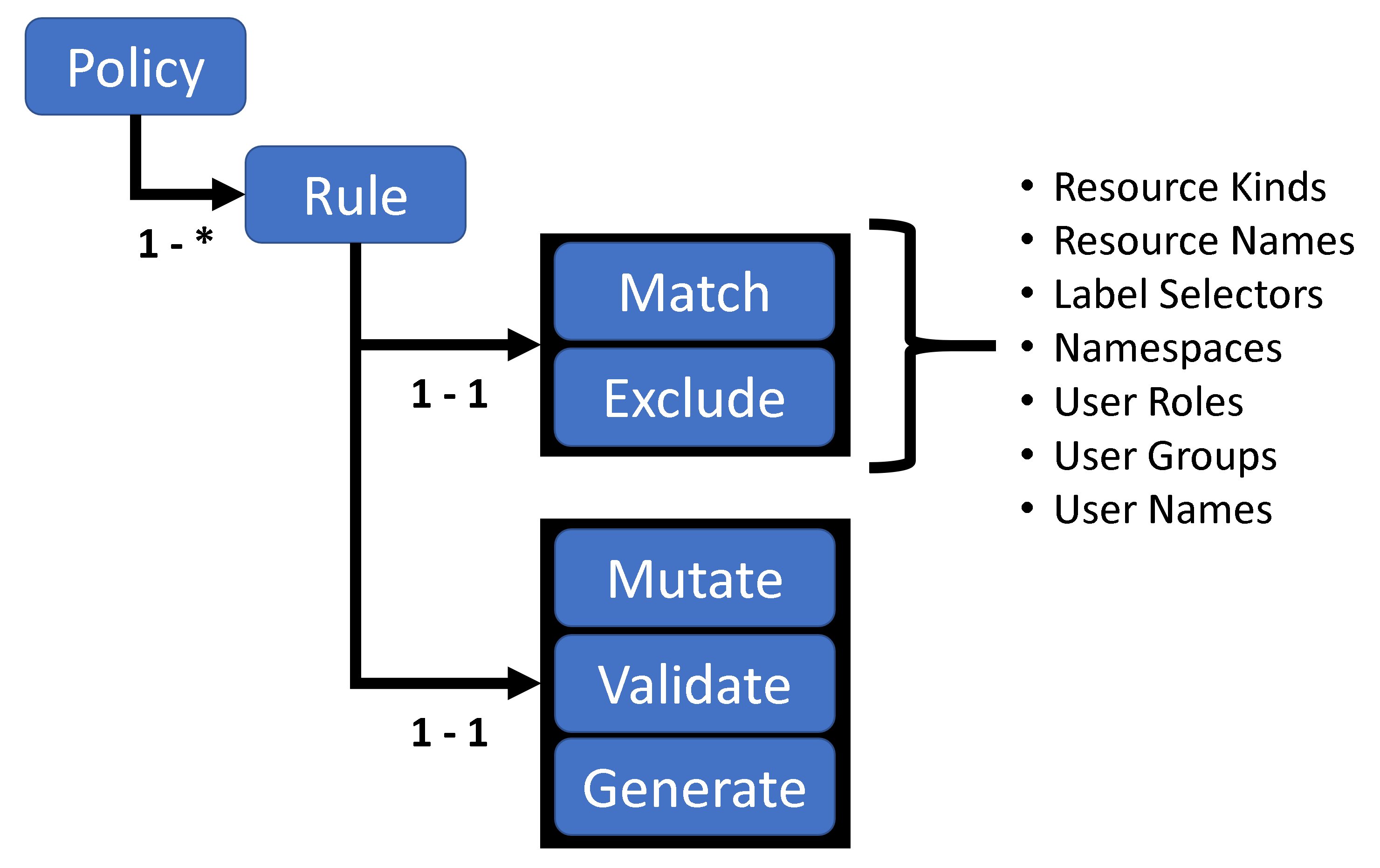
Each Kyverno policy contains one or more rules. Each rule has a `match` clause, an optional `exclude` clause, and one of a `mutate`, `validate`, or `generate` clause.
The match / exclude clauses have the same structure, and can contain the following elements:
* resources: select resources by name, namespaces, kinds, and label selectors.
* subjects: select users, user groups, and service accounts
* roles: select namespaced roles
* clusterroles: select cluster wide roles
When Kyverno receives an admission controller request, i.e. a validation or mutation webhook, it first checks to see if the resource and user information matches or should be excluded from processing. If both checks pass, then the rule logic to mutate, validate, or generate resources is applied.
The following YAML provides an example for a match clause.
````yaml
apiVersion : kyverno.io/v1
kind : ClusterPolicy
metadata :
name : policy
spec :
# 'enforce' to block resource request if any rules fail
# 'audit' to allow resource request on failure of rules, but create policy violations to report them
validationFailureAction: enforce
# Each policy has a list of rules applied in declaration order
rules:
# Rules must have a unique name
- name: "check-pod-controller-labels"
# Each rule matches specific resource described by "match" field.
match:
resources:
kinds: # Required, list of kinds
- Deployment
- StatefulSet
name: "mongo*" # Optional, a resource name is optional. Name supports wildcards (* and ?)
namespaces: # Optional, list of namespaces. Supports wildcards (* and ?)
- "dev*"
- test
selector: # Optional, a resource selector is optional. Values support wildcards (* and ?)
matchLabels:
app: mongodb
matchExpressions:
- {key: tier, operator: In, values: [database]}
# Optional, subjects to be matched
subjects:
- kind: User
name: mary@somecorp.com
# Optional, roles to be matched
roles:
# Optional, clusterroles to be matched
clusterroles: cluster-admin
...
````
Each rule can validate, mutate, or generate configurations of matching resources. A rule definition can contain only a single **mutate**, **validate**, or **generate** child node. These actions are applied to the resource in described order: mutation, validation and then generation.
---
*Read Next >> [Validate Resources](/documentation/writing-policies-validate.md)*